Global Impact of Climate Change
GLOBAL IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGE
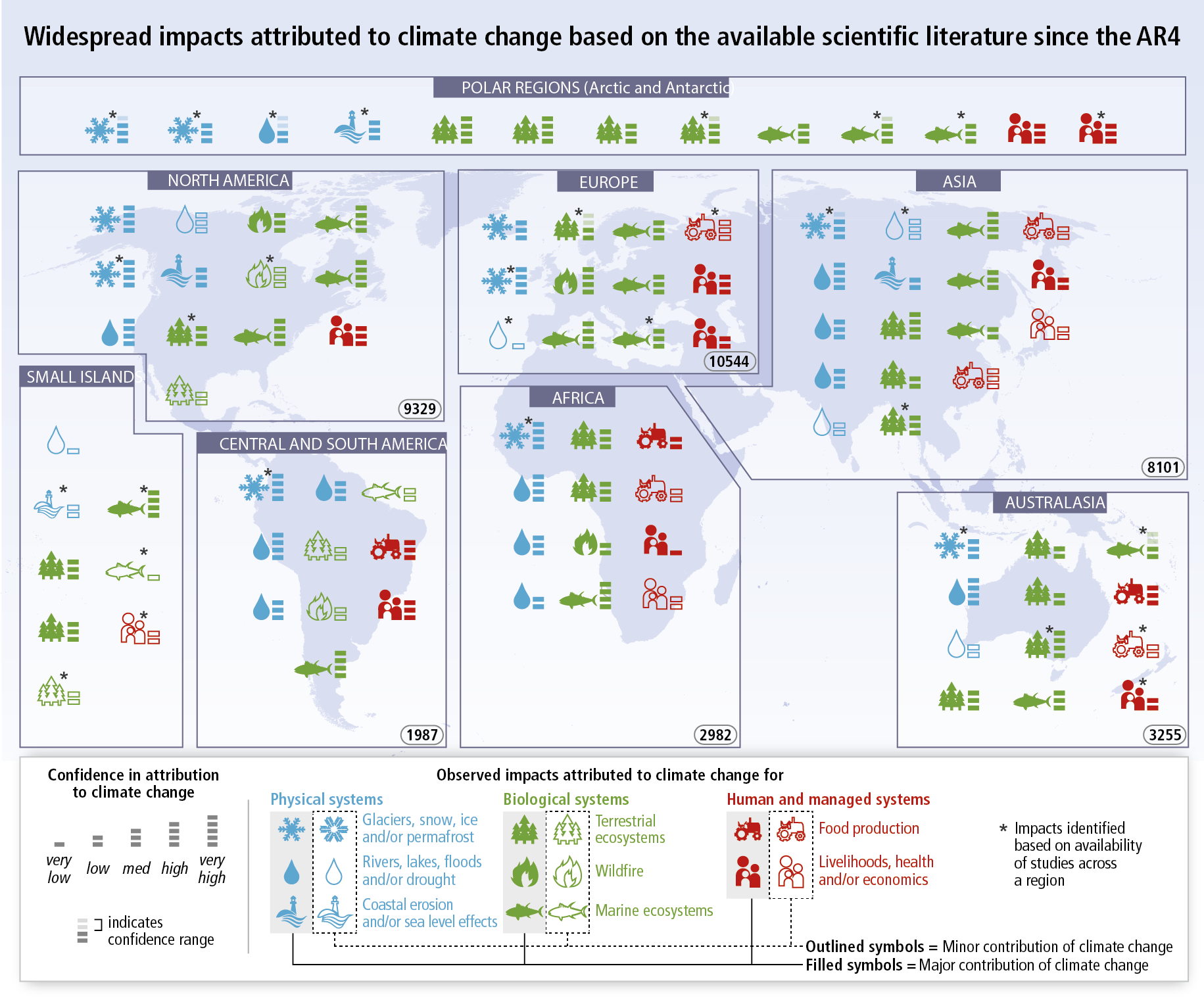
The Earth’s air, water and land are all linked to the climate. Any small increase in global average temperature over an extended period can trigger a chain reaction of climatic change around the world. Less rain can lead to drought, while too much rain can lead to flooding. More hot days during the year can dry up crops and affect people, plants and animals. In many places, people will struggle to cope with the changing environment.
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s (IPCC) Working Group I Sixth Assessment Report (released on 6 August 2021), world average surface temperatures could increase by 1.0°C to 5.7°C by the end of this century. The rate of global mean sea level rise has accelerated and will continue throughout the 21st century, ranging from 0.32m to 1.01m.
 2021 was Singapore’s second wettest year since 1980, with higher-than-average rainfall for most months and annual total rainfall of 2809.6mm at the Changi climate station. (From “2021 Climate and Weather: The Year in Review”, NEA)
2021 was Singapore’s second wettest year since 1980, with higher-than-average rainfall for most months and annual total rainfall of 2809.6mm at the Changi climate station. (From “2021 Climate and Weather: The Year in Review”, NEA)
Global Consequences
While a localised temperature change of 2°C or 3°C may not seem serious, it has grave consequences on a global scale because this temperature increase directly impacts the sustainability of water, food supplies, ecosystems, coastal stability and public health.
The following diagram summarises the environmental impact created by an increase in the global average annual temperature :